Small Size, Maximum Strength: Neodymium Magnet Grades Explained
We get it. You're searching for that tiny magnetic component that defies its size—something with enough sheer holding power to lock a mechanism, sense a position, or secure a critical assembly. It's tempting to believe the answer lies in a simple, top-tier grade like N52,N54. But sourcing the truly strongest “small neodymium magnets” demands moving beyond that single number. The real challenge isn't finding maximum strength; it's engineering that strength to survive and perform in your product's world.
Beyond the N52 Label: A Practical Perspective on "Peak" Strength
Let us begin with the fundamentals. Neodymium magnets are segmented into performance grades—N42, N45, N50, N52 and N54—with each grade corresponding to the magnet’s magnetic energy density. For micro-sized neodymium magnets, where spatial efficiency is a top priority, N54 currently leads the pack as the highest-performing option, delivering unparalleled pulling force relative to its compact dimensions.
But here’s a real-world truth we’ve learned firsthand: Highest energy product doesn’t always mean best performance for your project. Think of N52 magnets as high-performance yet delicate instruments, much like a ceramic component in a precision mechanism. While they generate immense magnetic force under optimal conditions, their inherent brittleness makes them vulnerable. Their granular structure can be prone to fracturing if subjected to impact or stress during use or assembly. Further, unlike N45 and N48 alternatives, N52 experiences irreversible magnetism degradation at comparatively mild temperature thresholds. I've watched projects stall when a brilliant design using a minuscule N52 disc faltered under the mild thermal load inside a sealed electronic housing. The solution wasn't a "stronger" magnet, but a smarter one—a marginally larger small rectangular neodymium magnet in N45 grade that maintained reliable force without succumbing to heat.
Geometry is Your Secret Weapon
The shape of your magnet fundamentally engineers its magnetic field. Choosing the right form is the first step to harnessing strength effectively.
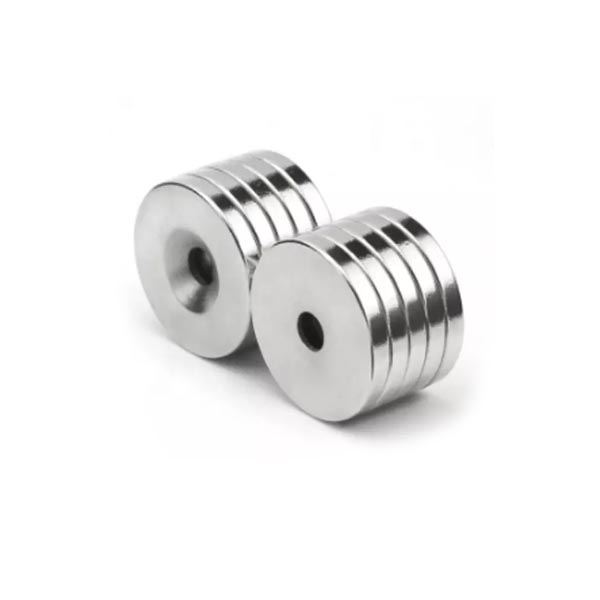
- Discs and Rings (small round neodymium magnets): Their flat poles create a wide, strong holding area perpendicular to the surface, perfect for latches or sensor triggers.
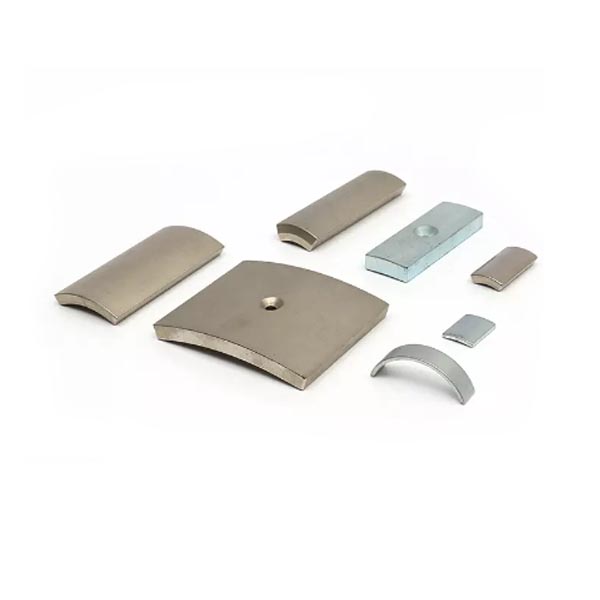
- Blocks and Squares (small square neodymium magnets): These provide a large grip surface, excelling in applications requiring resistance to sliding or shear forces.
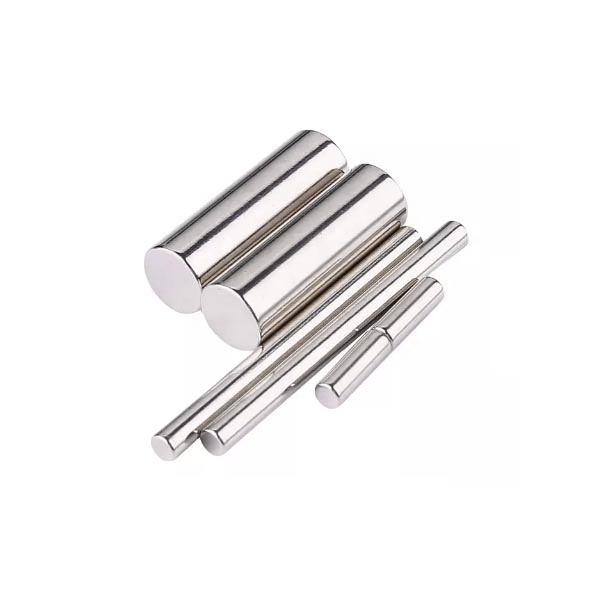
- Cylinders and Thin Bars (small 2x1 neodymium magnets): Their shape projects a deep, concentrated field, ideal for reaching into gaps or creating focused sensing zones.
The pivotal point? Each of these "industrial magnets" shapes can be precision-engineered from N54 material. Your initial focus should be: "What shape delivers the force "where and how" I need it?"
The Critical, Overlooked Details
Specifying the grade and shape is just the draft. The final specification—what separates success from failure—is in these details:
Your Target Material Isn't Always Steel: Published pull force data uses ideal, thick steel. If your magnet must grip "stainless steel, aluminum, or thin ferrous sheets", expect a dramatic reduction—sometimes over 50%. This miscalculation is a frequent root cause of underperformance.
Coating is More Than Cosmetic: The nickel coating on many "small neodymium disc magnets" provides basic protection. But for components facing humidity, condensation, or chemical exposure, an epoxy coating forms a far superior barrier against corrosion, despite its less shiny appearance.
Direction of Magnetization: A magnet's field has a specific axis. Standard discs are magnetized axially (through the flat faces). For a motor or a magnetic coupling, you might need a radial field. Clearly specifying this "magnetization direction" is crucial.
The Inescapable Impact of Heat: Ambient temperature is a key driver. The powerful hold of standard N52 begins to fade around 80°C. For environments near heat sources or in sun-exposed enclosures, you must specify magnets with higher maximum operating temperature ratings from the outset.
A Step-by-Step Specification Blueprint
Navigate the selection process with this actionable plan:
1. Function First: Pinpoint the primary role: Is it for static holding, motion conversion, precise positioning, or data sensing? This dictates the optimal geometry.
2. Grade with Context: Choose N52 if minimizing size is paramount and the operating environment is benign. If the application involves shock, vibration, or elevated temperatures, the intrinsic toughness of N45 or N48 grades often leads to a more robust and reliable solution.
3. Detail the Environment: Explicitly inform your supplier about any exposure to moisture, chemicals, oils, or temperature cycles. This determines the necessary coating and potential need for specialized high-temp grades.
4. Validate with Tangible Proof: Never approve a bulk order for small neodymium magnets for sale without real-world testing. Reputable suppliers expect and support this, offering working samples (small neodymium disc magnets, small rectangular neodymium magnets, etc.) for you to evaluate in actual conditions.
Identifying a True Manufacturing Partner
Your magnet supplier should be a source of solutions, not just products. The right partner will:
Probe with Purpose: They ask in-depth questions about your assembly process, end-use environment, and performance expectations.
Embrace True Customization: They can tailor dimensions, coatings, and magnetization beyond a standard catalog, viewing your specs as a starting point for optimization.
Demystify Quality Control: They openly explain their production batch testing protocols for magnetic strength, dimensional accuracy, and coating integrity.
Offer Preventative Insight: They review your requirements with an engineer's eye, proactively flagging potential issues like insufficient shear strength or thermal limitations before tooling begins.
The Smart Bottom Line
At the end of the day, compact high-strength neodymium magnets hit their maximum raw strength level with the N54 grade, which you can source in all the core configurations: discs, blocks, rings, and cylinders. That said, the best choice for your project isn’t just about brute force—it’s about finding the sweet spot between maximizing pulling power and making sure the magnet holds up to temperature shifts, physical wear, and other real-world stresses.
Invest your effort in a thorough analysis of the application's demands. Then, collaborate with a manufacturer who provides expert guidance through these material and engineering trade-offs. This approach secures "powerful magnets" that deliver not only exceptional initial performance but also sustained, dependable operation throughout your product's lifecycle.
Your Custom Neodymium Magnets Project
We can offer the OEM/ODM services of our products. The product can be customized according to your personalized requirements, including the size, Shape, performance, and coating. please offer your design documents or tell us your ideas and our R&D team will do the rest.
Other Types of Magnets
Post time: Dec-11-2025